05 Apr The science of healthy vinegar
In developing YourACV, we’re really dedicated to being the thought leaders in healthy drinking vinegars. It’s tricky, because vinegar does have some really great functional properties, but you’ll also read a lot of hype and myths about it from other sources. The great news for us no-nonsense types is that recent years have seen a lot more interest in this ancient food ingredient and the science behind it, so we’re really starting to understand the mechanisms that make apple cider vinegar as good as it is for you.
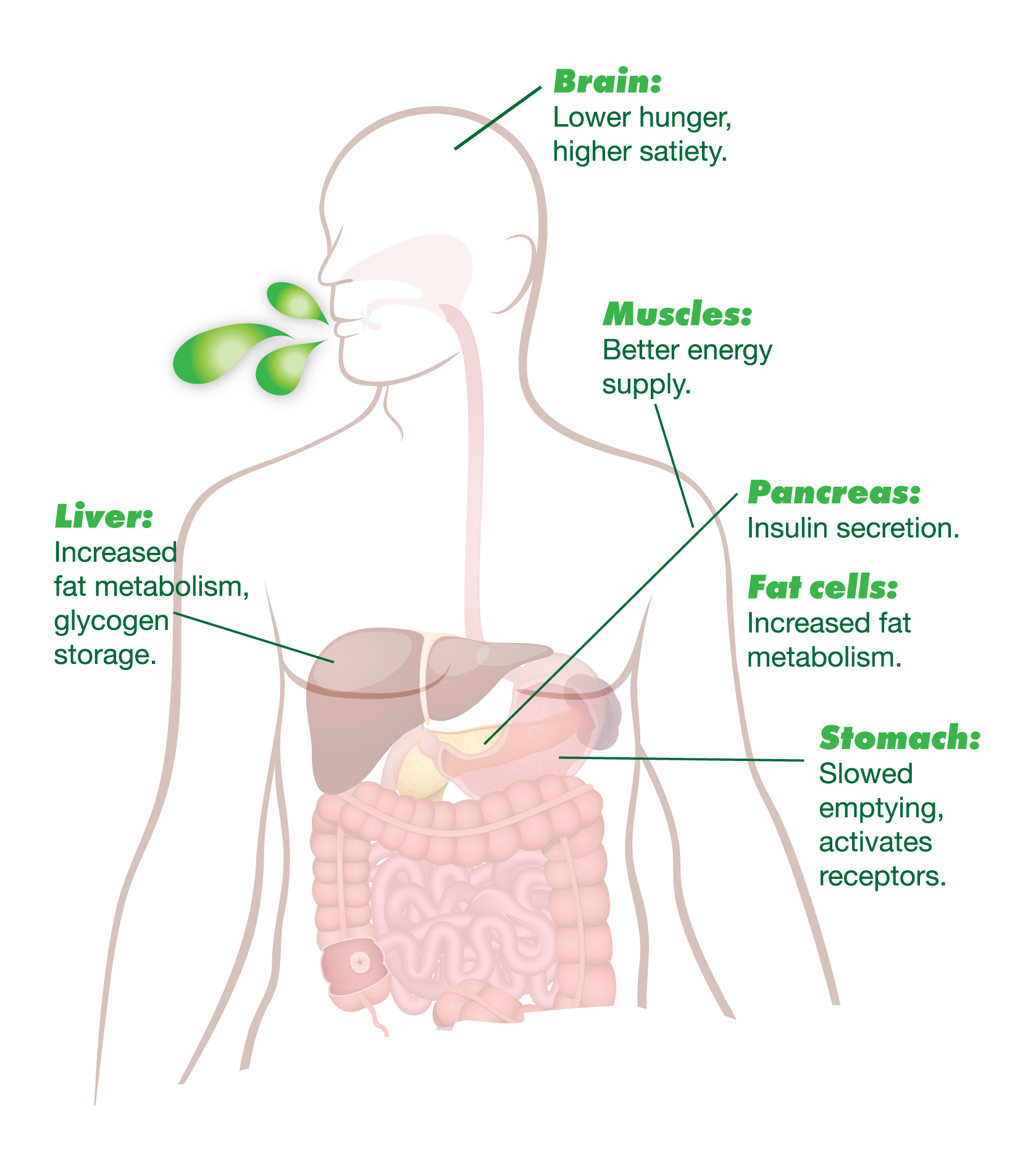
For starters, the acetic acid in vinegar can trigger free fatty acid receptors in your stomach, which in turn makes your body deal with food differently. It slows gastric emptying, increases feelings of fullness, activates fat metabolism in the liver, and causes vasodilation that makes your muscles feel fitter. Your body basically reacts as if it’s had a big, high energy meal, but without gaining the calories.
Digestion
When receptors in your stomach detect the natural vinegar in YourACV, several good things can happen. First, your body produces enzymes that let other parts know what’s up. Your stomach slows a little just to regulate the glucose from your meal and make your energy last longer, and your brain is filled with feelings of satisfaction and fullness.
Natural vinegars like that in YourACV also trigger heightened insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake, which helps in the vital role of energy expenditure.
Fat metabolism
As far as your body’s concerned, YourACV looks like broken down fats and sugars, but in this case the work has been done by our acetobacter before it even hits the bottle.
When your body detects the acetate from YourACV, it activates processes that decrease the production of body fat, increase the oxidation of fats and removes free fatty acids from circulation.
Wellness
Apart from increasing feelings of satiety and fullness, the acetate in YourACV can boost NO levels and insulin activity, which lead to beneficial vasodilation, allowing your body to circulate energy more easily. This can make you feel more vital and responsive, but is also important to cardiovascular health.


No Comments