ACV Science
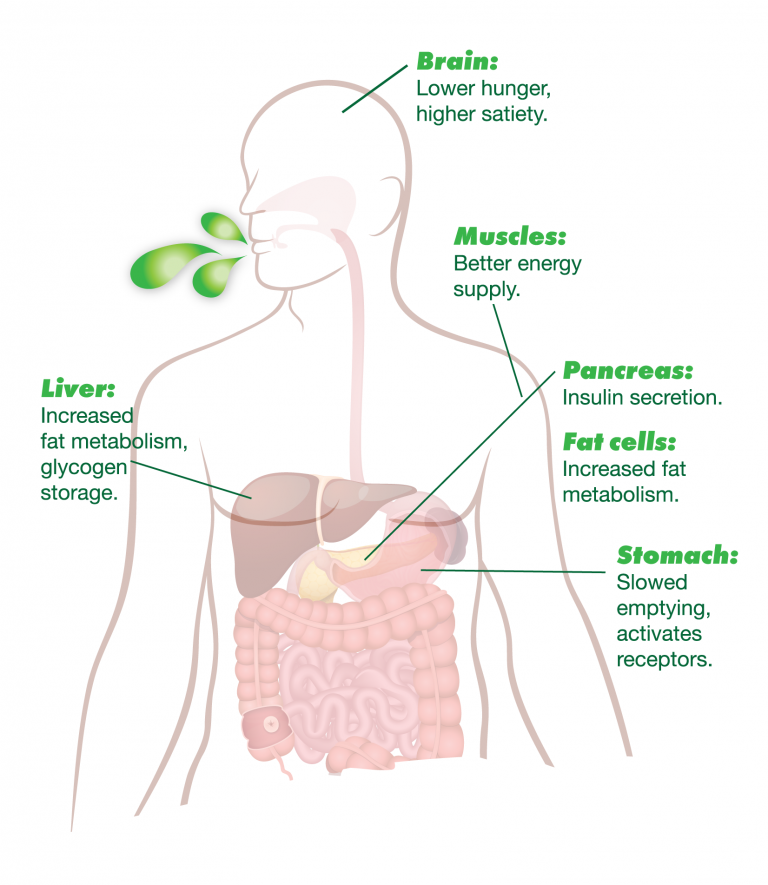
The acetic acid in vinegar can trigger free fatty acid receptors in your stomach, which in turn makes your body deal with food differently. It slows gastric emptying, increases feelings of fullness, activates fat metabolism in the liver, and causes vasodilation that makes your muscles feel fitter. “Your body basically reacts as if it’s had a big fatty meal, but without gaining the calories.
Your Fat Metabolism
As far as your body’s concerned, yourACV looks like broken down fats and sugars, but in this case the work has been done by our acetobacter before it even hits the bottle. When your body detects the acetate from yourACV, it activates processes that decrease the production of body fat, increase the oxidation of fats and removes free fatty acids from circulation.